What is a surfactant?
2023-07-14WIKI
A surfactant is a substance that reduces the surface tension of the medium significantly and hence improves the wetting behaviors or charged states of the particles. A surfactant is commonly used as a dispersing agent to prevent particles from agglomerating. Sodium hexametaphosphate and sodium pyrophosphate are commonly used in laser diffraction particle size analysis for the separation of particles that are easy to agglomerate in water.
The application of a surfactant made of alkylbenzene sulfonate allows a full dispersion of fine graphite particles in water, which facilitate the measurement procedure. Alkylbenzene sulfonate is readily available that can be obtained from soap or detergent.
The schematic below shows the preparation of the surfactant with sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) from dish detergent and the dispersion effect of graphite after introducing different amounts of surfactant.
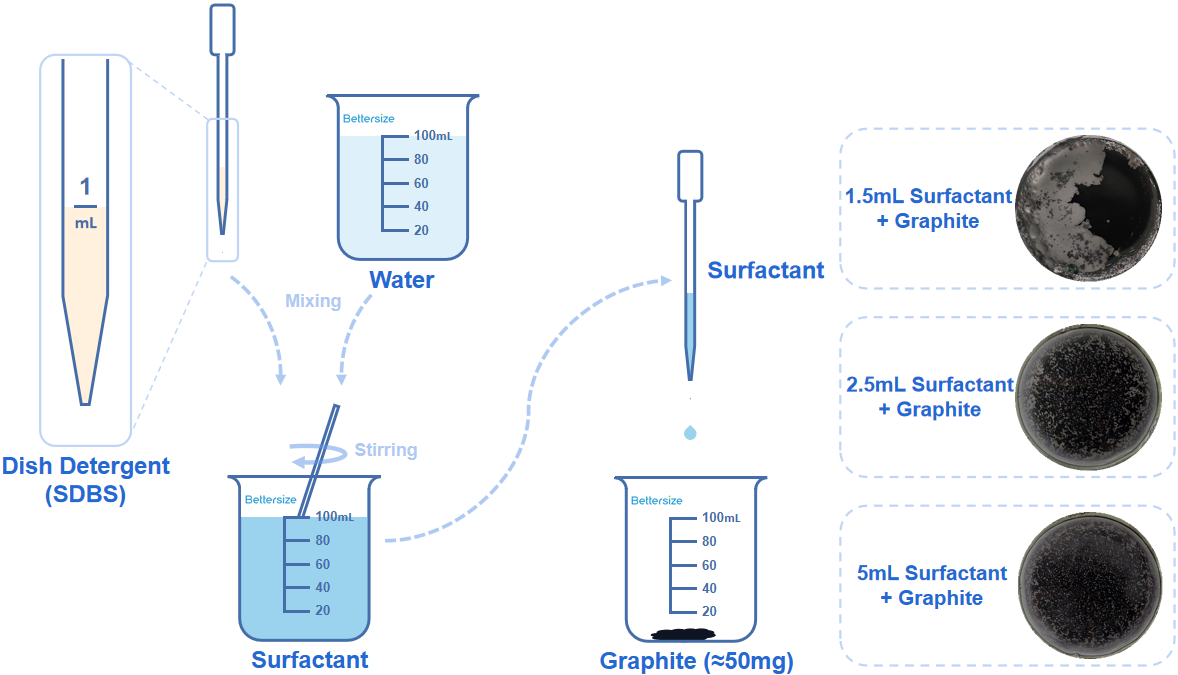
For more infomation, please check out Sample preparation guide for wet measurement using the laser diffraction particle size analyzer




